Hello all, as you all are aware that with the changing scenario and time, LINUX finds its place in general public home systems. It is now considered a comparable OS to windows or rather is better than windows in various ways.
So, in this article we are going to discuss about installing a Linux based OS along with windows. Initially it is better to perform dual boot or (play Linux on Virtual machine) if you are facing any difficulty in leaving windows at once.
Though it is useful to dual boot .However, you need to exercise caution during the setup process. First, make sure that you’ve backed up any important data on your Windows installation. Since you’ll be modifying your hard drive, you’ll want to store this backup on external media.
Now when you are backed up your data, Let's start with the process:
The objective here is to show how to install it on an HDD alongside an existing installation of Windows 7,with the Windows 7 boot manager as the “master” boot loader, so that at the end, when the computer is (re)booted, you will be presented with a boot menu that looks just like the one shown below.
You can download Kali image from here.
1. The first step is to make a separate partition for kali so that it will not create problem to windows installed. This can be done in Disk Management (type "diskmgmt.msc" in Run(Win key+R) window) in your PCs.
2. After shinking any of your drive you have some free space in your hard drive to install kali(you can create new partition here also), we will create new partitions while installing kali.
Install Kali Linux: The best option to select on Kali Linux’s boot menu is Graphical Install. It gives you a point-and-click installation process.
3. The next screen will ask you to select your preferred language, you can use the mouse to select this, then click Continue.

4. On the next screen, select your location and hit Continue.
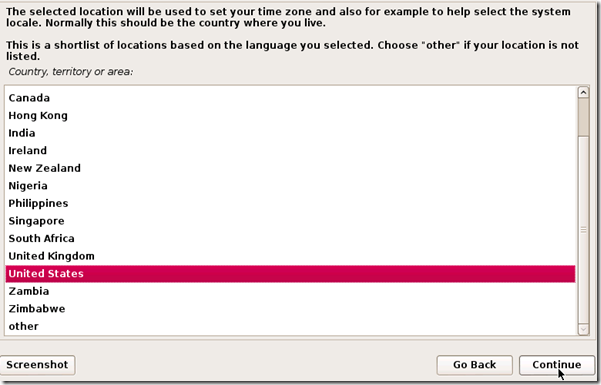
It’ll now ask you for your standard keymap. If you use the standard American English keyboard, then just click Continue.
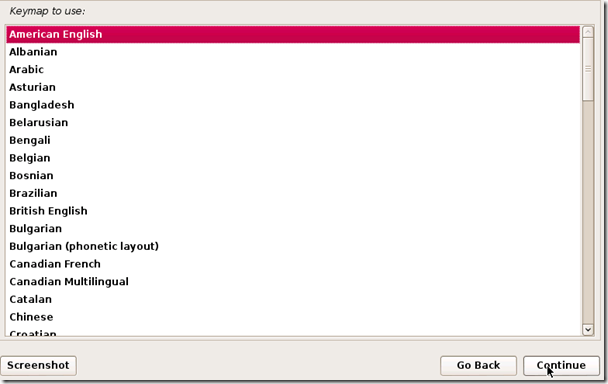
5. You will now be asked to supply a hostname, which is kind of like a computer name. You can enter anything you want, or you can just leave it as kali. When you’re done, hit Continue.
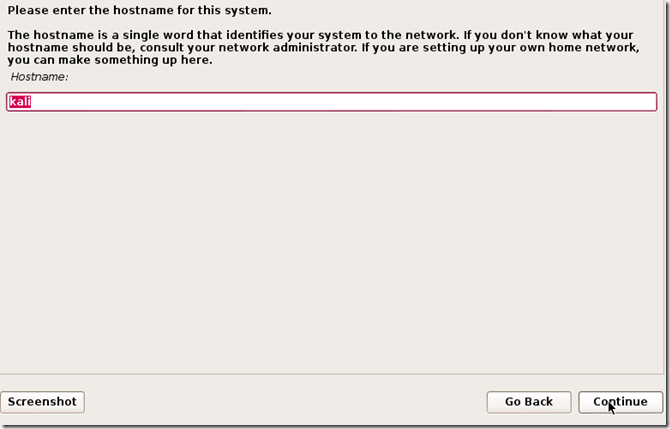
6. Kali will now ask you to enter a password for the root (main) account. Hit Continue after you’ve enter and re-entered the password of your choice.

7.
For installing Kali Linux, the following partitions will be created: /boot, /, /home, and Swap. In that order. The /home partition is optional. At the disk partitioning methods step of the installation process, you get a bunch of options. Because none of the guided options will create a separate /boot partition, creating the partitions will have to be done manually.
Select “Manual” and click Continue.

8. Here you can see the existing Windows 7 partitions, both of which are primary partitions. The free space, reclaimed from Windows 7 in the previous step is what will be used for creating the partitions for Kali Linux. To start creating the partitions, select the free space and click Continue.
9. Create a new partition. Continue.
10. This shows the total amount of disk space available for Kali Linux. The /boot partition will be created first, so you need to specify the amount of disk space for it.
11. For this test system, I assigned 300 MB to it. Continue.
12. Next
13. This step shows the details of the boot partition you just created. The only thing you need to change here is the mount point. Double-clicking on it will open another window where you can specify the correct mount point.
14.Here’s what it should look like after the mount point has been specified.
15. Here’s the final details of the boot partition. Scroll to “Done setting up the partition,” then click Continue. Note that the steps you used to create the boot partition will be repeated for the other partitions.
16. Back to the main disk partitioning window, you can see the boot partition you just created, plus the remaining free space. Select, the free space, then click Continue.
17. The next partition will be mounted at /. A new installation of Kali Linux takes up about 6.4 GB of disk space, so any amount greater than that will do. About 10-12 GB is more than enough but you can make it according to your wish. Continue.
18.Here are the details of the new partition. Scroll to “Done setting up the partition,” then click Continue.
For the home partition, I gave it a disk space of 100 GB. Continue.
Here are the details of the new partition. Scroll to “Done setting up the partition,” then click Continue.
19. For Swap, 2 GB is good enough. Continue.
20.Here are the default details of the new partition. To specify that it be used as a Swap partition, double-click the “Use as” line.
21. Then select “swap area.” Continue.
22. Scroll to “Done setting up the partition,” then click Continue.
23. With all the partitions created, scroll to “Finish partitioning and write changes to disk.” Continue. Make note of the device number of the boot partition. Here, it is sda5. You’ll need it later.
Select “Yes.” Continue.
24. By default, the installer will want to install GRUB, the boot loader, in the Master Boot Record (MBR). However, for setting up this dual-boot system, we want GRUB in the boot partition. So, select “No.” Continue.
This is where you have to specify where GRUB should be installed. For this test system, it is /dev/sda5.Continue.
After installation, the computer will reboot into Windows 7. The next task involves add an entry for Kali Linux in Windows 7′s boot menu.
Add Kali Linux to Windows 7′s boot menu:
The simplest graphical application for modifying the Boot Configuration Data of Window is EasyBCD. It is free for personal use. You may download it from here. Install it as you would any other Windows application. The main window is shown below. To add an entry for Kali Linux in the boot menu, click on the Add New Entry tab.
Then click on the Linux/BSD tab. From the Type dropdown menu, select GRUB 2. Modify the name field to reflect the name of the distribution you are adding. From the Drive menu, you can either select the specific partition corresponding to the boot partition of the Kali Linux installation or let EasyBCD automatically locate and load it. Either one will work. Note that EasyBCD’s drive numbers and the device numbers of the Linux partitions do not match. For example, in this test installation, the boot partition is /dev/sda5, but the corresponding drive number in EasyBCD is Partition 3. The size of the partition helps to determine which one it is. Click theAdd Entry button when wll the options have been specified.
From the Edit Boot Menu tab, you can see a preview of the entries that will appear in the Windows 7 boot menu. Exit EasyBCD and reboot the computer. That should do it.
Here! We are done with installation process. Enjoy working on Linux.
Thank you!!


No comments:
Post a Comment